Introduction
The business landscape is experiencing a fundamental transformation as artificial intelligence agents evolve from simple chatbots into sophisticated digital employees capable of complex reasoning, decision-making, and autonomous action. In 2025, AI agents will represent one of the most significant technological shifts in how organizations operate and deliver value.
Market Growth and Adoption
The AI agents market reached $4.8 billion in 2024 and is projected to grow to $28.5 billion by 2030, representing a 34.2% compound annual growth rate. According to Gartner’s latest AI market research, enterprise adoption continues to accelerate. Key adoption statistics include:
- 67% of large enterprises have deployed or are actively piloting AI agents
- 89% plan implementation within the next 18 months
- Organizations report 45-70% productivity gains and 25-40% cost reductions, as confirmed by McKinsey’s AI adoption survey which reveals significant productivity improvements across industries
- Customer satisfaction scores improve by an average of 28% with proper implementation
Forrester’s AI agents market analysis projects continued exponential growth through 2030, supporting these market projections.
Technological Catalysts
Several breakthroughs enable current-generation business AI agents:
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Advanced models like GPT-4 and Claude provide unprecedented natural language understanding.
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG): Allows agents to access vast organizational knowledge using frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex.
- Multi-Modal Capabilities: Modern agents process text, images, audio, and video
- Tool Integration: Agents interact with business systems, APIs, and databases
This guide is part of our comprehensive AI automation series – explore our complete resource library at the bottom of this page.
Understanding AI Agents
Definition and Evolution
An AI agent is an autonomous software system that perceives its environment, processes information using AI capabilities, makes decisions based on goals, and takes actions to achieve specific objectives. Unlike traditional software requiring explicit programming, AI agents use reasoning, learning, and adaptation.
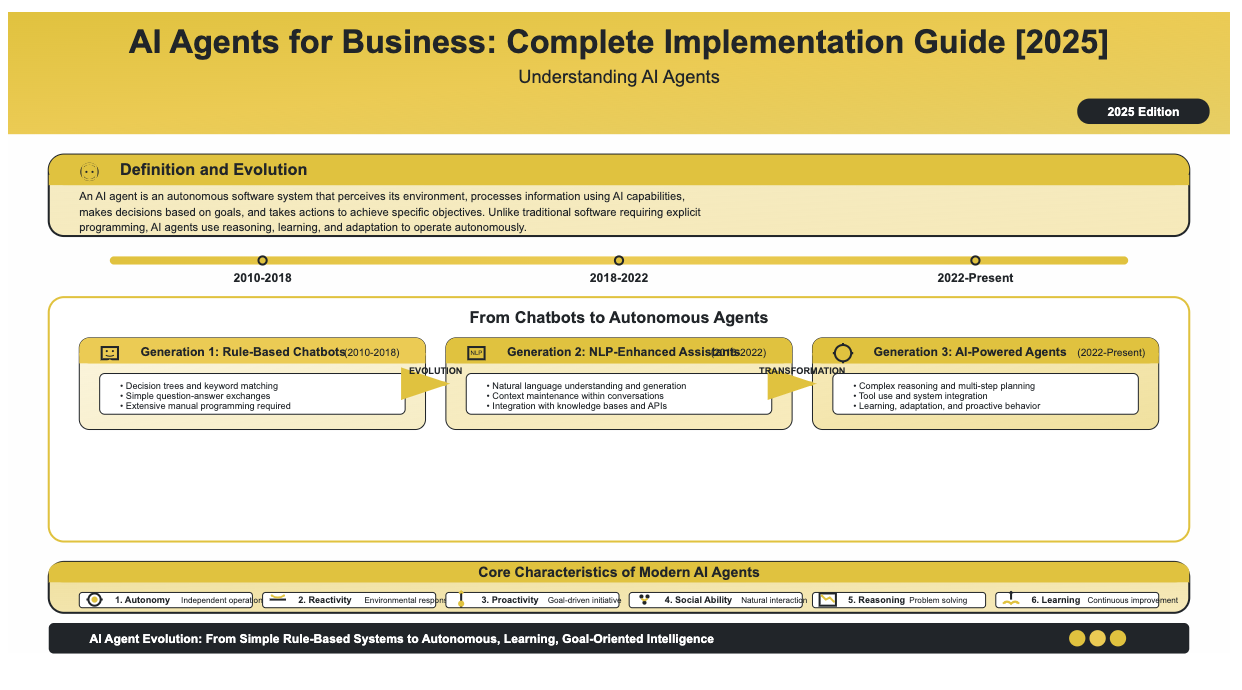
From Chatbots to Autonomous Agents
Generation 1: Rule-Based Chatbots (2010-2018)
- Operated on decision trees and keyword matching
- Limited to simple question-answer exchanges
- Required extensive manual programming
Generation 2: NLP-Enhanced Assistants (2018-2022)
- Natural language understanding and generation
- Context maintenance within conversations
- Integration with knowledge bases and APIs
Generation 3: AI-Powered Agents (2022-Present)
- Complex reasoning and multi-step planning
- Tool use and system integration
- Learning and adaptation from interactions
- Proactive behavior and goal pursuit
Core Characteristics
Modern AI agents possess six defining characteristics:
- Autonomy: Operate independently with minimal human oversight
- Reactivity: Perceive and respond to environmental changes
- Proactivity: Take initiative to achieve goals
- Social Ability: Interact naturally with humans and other agents
- Reasoning and Planning: Break down complex problems and develop solutions
- Learning and Adaptation: Improve performance through experience
Types of Business AI Agents
Customer-Facing Agents
Customer Service and Support
- Omnichannel Integration: Seamless support across web, mobile, social media, email, and voice
- Intelligent Issue Resolution: Multi-step troubleshooting with adaptive questioning
- Escalation Management: Smart routing to human agents when needed
- Personalization: Adaptation to individual communication styles and preferences
E-commerce and Sales Support
- Product Recommendation: Understanding needs and suggesting appropriate solutions
- Transaction Facilitation: End-to-end order management and payment processing
- Customer Onboarding: Interactive tutorials and feature discovery
Employee-Supporting Agents
HR and People Operations
- Policy Assistance: Natural language explanation of complex HR policies
- Benefits Navigation: Comprehensive guidance on employee benefits
- Career Development: Skill assessment and learning path recommendations
- Administrative Automation: Expense processing, time tracking, document management
IT Support and Technical Assistance
- Troubleshooting: Step-by-step problem resolution
- Access Management: Password resets and account provisioning
- Knowledge Management: Access to technical documentation and training
Operations and Process Agents
Supply Chain and Logistics
- Demand Forecasting: AI-powered prediction of inventory needs
- Automated Procurement: Purchase order generation and vendor selection
- Route Optimization: Cost and time-efficient delivery planning
Quality Assurance and Compliance
- Process Monitoring: Continuous quality indicator tracking
- Regulatory Compliance: Real-time monitoring for compliance adherence
- Risk Mitigation: Proactive identification and resolution of compliance risks
Data Analysis Agents
Business Intelligence and Analytics
- Real-Time Processing: Live dashboard management and anomaly detection
- Custom Reporting: Automated and ad-hoc analysis generation
- Decision Support: Scenario modeling and risk assessment
Anatomy of an Effective AI Agent
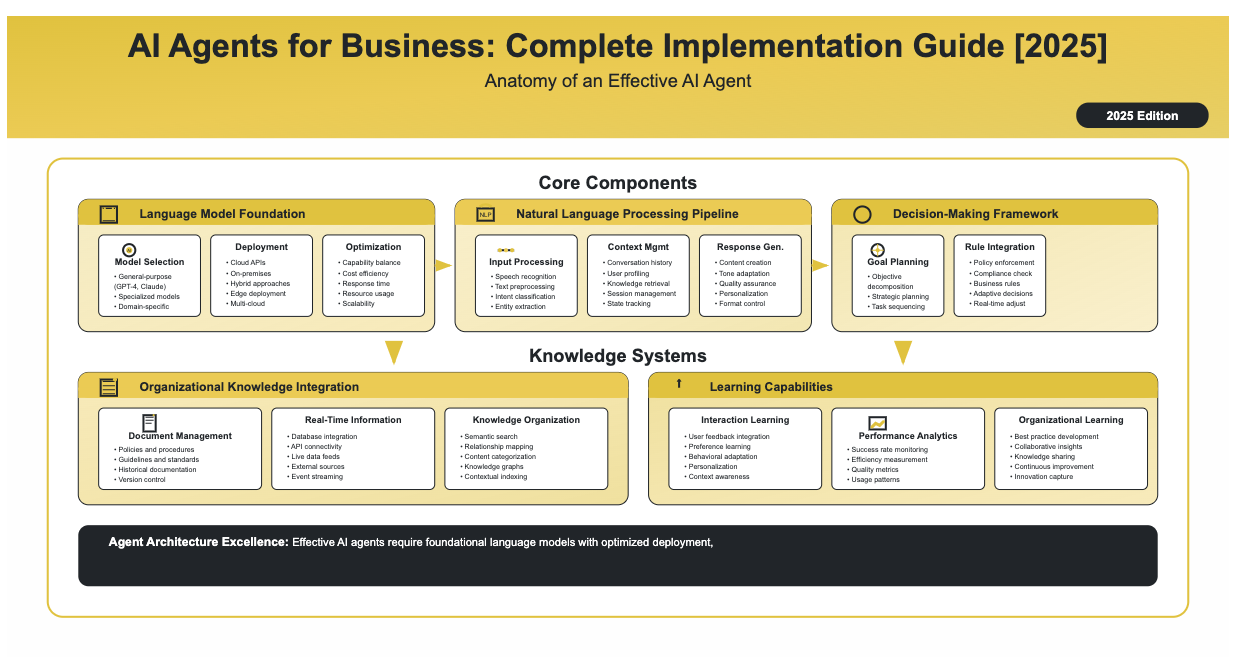
Core Components
Language Model Foundation
- Model Selection: Choose between general-purpose (GPT-4, Claude) or specialized models
- Deployment Strategy: Cloud APIs, on-premises, or hybrid approaches
- Performance Optimization: Balancing capability, cost, and response time
Natural Language Processing Pipeline
- Input Processing: Speech recognition, text preprocessing, intent classification
- Context Management: Conversation history, user profiling, knowledge retrieval
- Response Generation: Content creation, tone adaptation, quality assurance
Decision-Making Framework
- Goal-Oriented Planning: Objective decomposition and strategic planning
- Business Rule Integration: Policy enforcement and compliance checking
- Adaptive Decision-Making: Real-time adjustment and feedback integration
Knowledge Systems
Organizational Knowledge Integration
- Document Management: Complete access to policies, procedures, and guidelines
- Real-Time Information: Database integration and API connectivity
- Knowledge Organization: Semantic search and relationship mapping
Learning Capabilities
- Interaction-Based Learning: User feedback integration and preference learning
- Performance Analytics: Success rate monitoring and efficiency measurement
- Organizational Learning: Best practice development and collaborative insights
Building AI Agents for Business
Assessment and Planning
Business Needs Analysis
- Process Identification: High-volume, standardized processes with clear outcomes
- ROI Assessment: Cost analysis, automation potential, and expected benefits
- Impact Evaluation: Customer pain points and employee efficiency opportunities
Technical Infrastructure Assessment
- System Integration: API availability and data accessibility
- Security Requirements: Compliance needs and data protection
- Performance Requirements: Response time, availability, and scalability needs
Organizational Readiness
- Stakeholder Alignment: Executive sponsorship and user acceptance
- Change Management: Cultural fit and transformation capability
- Resource Assessment: Technical expertise and training requirements
Development Approaches
Platform-Based Development
Major Platforms:
- Microsoft Bot Framework: Azure integration and enterprise features
- Google Dialogflow: Advanced NLP with Google Cloud integration
- Amazon Lex: AWS integration with strong voice capabilities
- Specialized Platforms: Rasa (open-source), Botpress (visual development)
Selection Criteria:
- Feature completeness against requirements
- Integration capabilities with existing systems
- Scalability and performance characteristics
- Cost structure and vendor support quality
Custom Development
- When to Choose: Unique requirements, competitive advantage, complex integration
- Considerations: Technical expertise required, longer timelines, ongoing maintenance
Testing and Training
Comprehensive Testing Framework
- Functional Testing: Conversation flows, intent recognition, integration validation
- Performance Testing: Response times, concurrent users, scalability using tools like Apache JMeter and LoadRunner
- User Acceptance: Business user validation and customer experience testing
Training Methodologies
- Dataset Development: Representative scenarios and diverse user inputs
- Continuous Training: Production data integration and feedback loops
- Quality Assurance: Training data accuracy and model updates
Industry-Specific Applications
Customer Service Transformation
Advanced Capabilities
- Intelligent Ticket Management: Multi-dimensional analysis and specialist routing
- Real-Time Resolution: Knowledge base integration and step-by-step guidance
- Proactive Communication: Issue prediction and preventive outreach
Sales and Marketing
Lead Qualification and Nurturing
- Intelligent Scoring: Multi-factor analysis and predictive conversion modeling
- Conversational Qualification: Natural discovery and needs analysis
- Personalized Automation: Behavioral targeting and campaign orchestration
HR and Employee Support
Comprehensive Self-Service
- Policy Guidance: Clear explanations and benefits navigation
- Career Development: Skill assessment and learning recommendations
- Performance Management: Goal setting and progress tracking
Operations Optimization
Supply Chain Intelligence
- Demand Planning: Multi-variable analysis and real-time sensing
- Inventory Optimization: Dynamic management and obsolescence prevention
- Quality Control: Process monitoring and automated corrective actions
Implementation Strategy
Organizational Readiness Assessment
Cultural and Change Readiness
- Leadership Commitment: Executive sponsorship and resource allocation
- Employee Acceptance: Technology comfort and job security concerns
- Workflow Integration: Process maturity and system complexity
Technical Infrastructure Evaluation
- System Architecture: Integration capabilities and security infrastructure
- Data Infrastructure: Quality, governance, and privacy compliance
- Skill Assessment: Internal expertise and training requirements
Integration with Existing Systems
Enterprise System Connectivity
- CRM Integration: Customer data unification and sales process integration
- ERP Integration: Financial systems and supply chain connectivity
- Communication Platforms: Omnichannel and knowledge management integration
User Adoption Strategies
Change Management Approach
- Communication Strategy: Following Kotter’s 8-Step Process and clear value proposition setting
- Training Programs: Role-specific training and hands-on practice
- Support Infrastructure: Help desk integration and peer support networks
Security and Compliance
Data Security Framework
- Information Protection: Encryption, access controls, data minimization
- Privacy Compliance: GDPR, CCPA, and industry-specific standards
- Authentication: Single sign-on, multi-factor authentication, audit trails
Measuring Performance
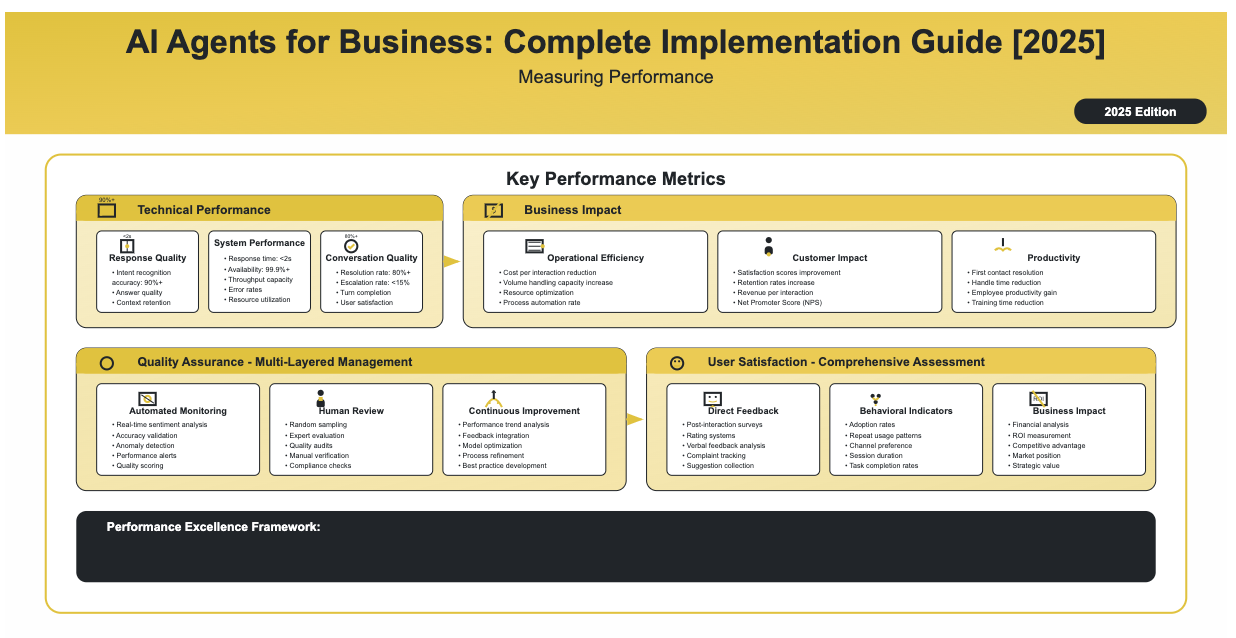
Key Performance Metrics
Technical Performance
- Response Quality: Intent recognition accuracy (target: 90 %+)
- System Performance: Response time (<2 seconds), availability (99.9 %+)
- Conversation Quality: Resolution rate (80 %+), escalation rate (<15%)
Business Impact
- Operational Efficiency: Cost per interaction, volume handling capacity
- Customer Impact: Satisfaction scores, retention rates, revenue per interaction
- Productivity: First contact resolution, handle time reduction, employee productivity
Quality Assurance
Multi-Layered Management
- Automated Monitoring: Real-time sentiment analysis and accuracy validation
- Human Review: Random sampling and expert evaluation
- Continuous Improvement: Performance trend analysis and feedback integration
User Satisfaction
Comprehensive Assessment
- Direct Feedback: Post-interaction surveys and rating systems
- Behavioral Indicators: Adoption rates, repeat usage, channel preference
- Business Impact: Financial analysis and competitive advantage assessment
Ethical Considerations
Transparency and Disclosure
Ethical Communication Framework
- Clear AI Identification: Explicit disclosure of AI agent interactions
- Capability Communication: Honest representation of limitations
- Informed Consent: Clear consent for data usage and interaction recording
Bias Detection and Mitigation
Comprehensive Prevention Framework
- Bias Identification: Training data auditing and algorithmic bias testing following NIST AI bias guidelines
- Mitigation Strategies: Data augmentation and fairness constraints using AI Fairness 360 tools
- Governance Controls: Diverse development teams and external auditing
Privacy Considerations
Data Protection Framework
- Data Minimization: Purpose limitation and retention policies
- Privacy-Preserving Technologies: Anonymization and differential privacy techniques
- User Rights: Access, correction, deletion, and portability rights under GDPR Article 20
Future of AI Agents
Emerging Capabilities
Next-Generation Technologies
- Advanced Reasoning: Multi-step reasoning and strategic thinking
- Multimodal Integration: Vision-language integration and spatial understanding
- Enhanced Autonomy: Goal-oriented autonomy and creative problem-solving
Regulatory Landscape
Evolving Governance
- Global Developments: EU AI Act, US policy evolution, international standards
- Compliance Requirements: Documentation standards, risk assessment, audit requirements
- Strategic Adaptation: Building compliance into design, future-proofing
Cross-System Orchestration
Enterprise Ecosystems
- Multi-Agent Coordination: Distributed intelligence networks and collaborative workflows
- Cross-Platform Integration: Vendor-agnostic orchestration and standards-based communication
- Ecosystem Optimization: System-wide optimization and adaptive configuration
Implementation Roadmap
Phase 1: Foundation and Assessment (Months 1-3)
- Organizational readiness evaluation
- Use case identification and prioritization
- Stakeholder alignment and initial planning
Phase 2: Pilot Implementation (Months 4-8)
- Pilot project execution with limited scope
- Performance monitoring and learning integration
- Capability development and user training
Phase 3: Scaled Deployment (Months 9-18)
- Gradual expansion across use cases
- Integration enhancement and performance optimization
- Advanced capability implementation
Phase 4: Enterprise Transformation (Months 18+)
- Organization-wide integration
- Multi-agent orchestration
- Innovation and strategic advantage
Key Success Factors
Critical Elements:
- Executive Commitment: Strong leadership support throughout implementation
- User-Centric Design: Focus on user needs over technology capabilities
- Iterative Approach: Start small, learn quickly, scale based on success
- Quality Focus: Maintain high performance and experience standards
- Ethical Implementation: Follow responsible AI principles
Getting Started Checklist
Immediate Actions
- Conduct an organizational readiness assessment
- Identify and prioritize high-value use cases
- Evaluate technical infrastructure requirements
- Assess skill gaps and training needs
- Develop a business case with ROI projections
- Establish a project team with appropriate expertise
- Secure executive sponsorship and resources
- Select an appropriate AI agent platform
- Plan the system integration architecture
- Define success metrics and measurement frameworks
Conclusion
AI agents represent a transformative opportunity for businesses to enhance efficiency, improve customer experience, and create competitive advantages. Success requires careful planning, systematic implementation, and commitment to ethical practices.
Organizations that master AI agent implementation will be well-positioned to thrive in an AI-driven business environment. The key lies in starting with clear objectives, building on proven foundations, and continuously learning and adapting as capabilities evolve.
The future belongs to organizations that can effectively combine human creativity and judgment with AI agent efficiency and scale, creating hybrid intelligence systems that deliver unprecedented business value while maintaining trust and ethical standards.
Comprehensive AI Automation Resources for Every Business Need
This implementation guide specializes in deploying autonomous AI agents across customer service, operations, and employee support functions.
Part of our complete AI automation resource library, this guide provides strategic frameworks for agent deployment across your organization.
From here, you can access our complete library of specialized resources that cover every aspect of AI automation strategy, implementation, and optimization.
Our structured guide series takes you from foundational concepts through advanced implementation strategies, ensuring you have the knowledge and frameworks needed for successful AI automation deployment at any scale.
Each specialized guide builds upon core concepts while diving deep into specific areas of AI automation, providing both strategic insights and practical implementation guidance tailored to your organizational needs and objectives.
Resources and Further Learning
Explore Our AI Automation Content Categories
Continue your exploration with our in-depth coverage of specific topics:
- AI Automation Fundamentals – Core concepts and foundational knowledge
- AI Workflow Automation – Process design and implementation strategies
- AI Agents & Assistants – Intelligent agent development and deployment
- Custom AI Solutions – Build vs. buy decisions and custom development
- Business Impact & ROI – Value measurement and business case development
Stay Updated on AI Automation Developments
The field of AI automation evolves rapidly. To stay current with the latest developments:
- Follow our blog for regular analysis of emerging trends and technologies
- Access our resource library for templates, frameworks, and implementation tools
- Join professional communities to connect with other practitioners
- Subscribe to industry publications for ongoing insights and updates
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
AI agents are autonomous software systems that can reason, plan, and take actions to achieve specific business objectives, while traditional chatbots simply respond to predefined scripts.
Modern AI agents possess six key capabilities: autonomy (operating independently), reactivity (responding to changes), proactivity (taking initiative), social ability (natural interaction), reasoning and planning (solving complex problems), and learning and adaptation (improving through experience).
Unlike Generation 1 rule-based chatbots that relied on decision trees, today’s AI agents use advanced language models to understand context, integrate with business systems, and handle multi-step processes autonomously.
Organizations typically see significant measurable improvements within 6-18 months of implementation.
Common results include 45-70% productivity gains, 25-40% cost reductions, and 28% average improvement in customer satisfaction scores.
The key is starting with high-volume, standardized processes that have clear success metrics and measurable outcomes.
The most successful AI agent implementations target processes that are high-volume, rule-based, and have clear success metrics.
Top-performing applications include customer service and support (omnichannel integration, intelligent issue resolution), HR operations (policy assistance, benefits navigation), IT support (troubleshooting, access management), sales support (lead qualification, product recommendations), and operations management (supply chain optimization, quality assurance).
The key is identifying processes where agents can provide immediate value while integrating seamlessly with existing workflows and systems.
Platform-based development is typically recommended for most organizations due to faster implementation, lower costs, and proven capabilities.
Major platforms like Microsoft Bot Framework, Google Dialogflow, and Amazon Lex offer enterprise features, strong integration capabilities, and vendor support.
Choose custom development only when you have unique requirements that provide a competitive advantage, complex integration needs that platforms can’t address, or sufficient technical expertise for ongoing maintenance.
Consider factors like feature completeness, integration capabilities, scalability, cost structure, and the quality of vendor support when making your selection.
Implementation follows a four-phase approach: Foundation and Assessment (Months 1-3) for readiness evaluation and planning, Pilot Implementation (Months 4-8) for limited-scope execution and learning, Scaled Deployment (Months 9-18) for gradual expansion and optimization, and Enterprise Transformation (Months 18+) for organization-wide integration.
Investment varies by scope and complexity, but organizations should budget for platform licensing, integration costs, training, and change management (typically 15-25% of total budget), as well as ongoing maintenance.
Most organizations see positive ROI within 12-18 months, with full value realization achieved by month 24.
These implementation fundamentals provide the foundation for successfully deploying AI agents that deliver measurable business value. For detailed technical specifications, industry-specific deployment strategies, and advanced optimization techniques, explore our comprehensive AI automation resources and specialized implementation frameworks.
About This Guide
This comprehensive guide is maintained by industry experts and researchers who work directly with organizations implementing AI automation solutions. Content is regularly updated to reflect the latest developments in technology, best practices, and industry applications.
Last Updated: June 2025
This guide represents analysis of current AI agents and best practices. Individual results may vary based on organizational context, implementation approach, and specific use cases.
Was this guide helpful?
